The yen carry trade, a popular financial strategy, is unraveling due to major shifts in Japan’s monetary policy. Here’s what you need to know:
- What is the yen carry trade? Traders borrow yen at low interest rates to invest in higher-yielding assets globally, profiting from the difference.
- Why is it unwinding? The Bank of Japan (BoJ) has raised interest rates to 0.75% and scaled back quantitative easing, making borrowing yen more expensive. Meanwhile, U.S. interest rates are falling, shrinking the profit margin.
- Impact on markets: The unwinding has led to sharp yen appreciation, global asset sell-offs, and increased market volatility. In August 2024, $200 billion in carry trades were liquidated in weeks, triggering a 12.4% Nikkei drop and U.S. tech stock declines.
- Key risks: Sudden yen strength, rising Japanese bond yields, and policy changes are pressuring traders, causing ripple effects across equities, bonds, and currencies.
- What to watch: USD/JPY levels near 155–156, Japanese bond yields above 2%, and volatility indicators like Bollinger Bands signal potential further unwinds.
Traders need to adjust strategies to navigate these shifts, focusing on risk management and reliable trading platforms to handle rapid market changes.
The Yen Carry Trade Explained with Examples and What Happens When It Unwinds (2025)
Past Yen Carry Trade Unwinds: What Happened
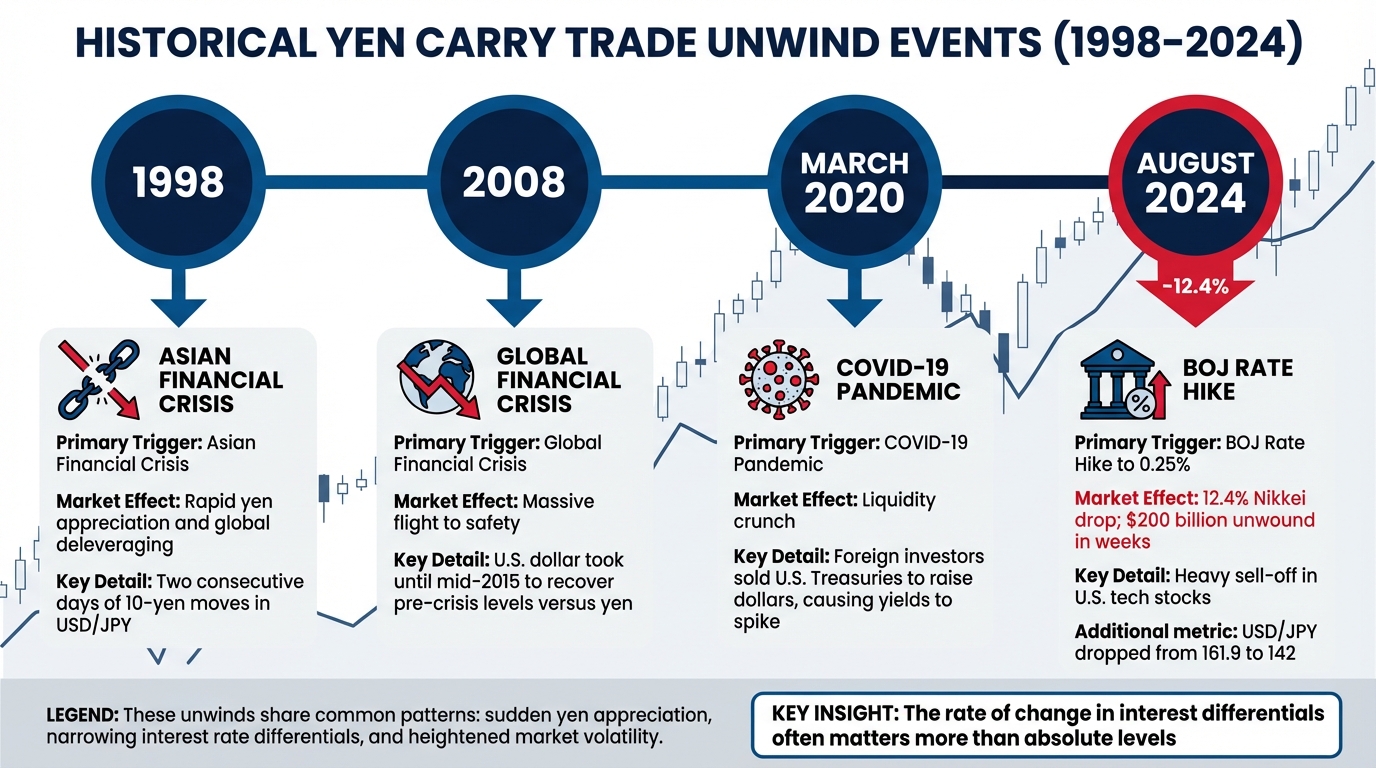
Historical Yen Carry Trade Unwinds: 1998-2024 Timeline and Market Impact
August 2024 Unwind: A Case Study
On July 31, 2024, the Bank of Japan raised its benchmark interest rate to 0.25% and announced plans to scale back its quantitative easing program. This policy shift, paired with a weak U.S. jobs report, set off a quick reaction in financial markets. The USD/JPY pair dropped sharply, moving from around 161.9 in early July to approximately 142 by August 5[8].
The turbulence didn’t stop there. On August 5, Japan’s Nikkei 225 plummeted by 12.4%, marking its steepest drop since 1987. The S&P 500 also took a hit, falling 3% on the same day. Speculative short positions, which had reached $31 billion in late June, were slashed to $15 billion by early August[7].
UBS analysts estimated that about $200 billion of carry trades – out of a total $500 billion – were unwound within just two to three weeks[2]. The dollar/yen overnight implied volatility surged to 27% in July 2024, signaling the scale of the market shake-up[8]. Many traders who had borrowed yen to invest in high-growth stocks faced forced liquidations, which put additional pressure on U.S. tech equities[3].
"How much the carry trade could unwind depends not so much on the level of the interest rate differential but the change in the interest rate differential." – James Malcolm, UBS Japan Macro Strategist[2]
What Past Unwinds Teach Us
This case study mirrors patterns seen in previous yen carry trade crises. Events like the 1998 Asian Financial Crisis, the 2008 Global Financial Crisis, and the March 2020 pandemic-induced liquidity crunch all shared common triggers. These included sudden yen appreciation, narrowing interest rate differentials, and heightened market volatility.
| Period | Primary Trigger | Market Effect |
|---|---|---|
| 1998 | Asian Financial Crisis | Rapid yen appreciation and global deleveraging; two consecutive days of 10-yen moves in USD/JPY[2][8] |
| 2008 | Global Financial Crisis | Massive flight to safety; U.S. dollar took until mid-2015 to recover pre-crisis levels versus yen[1] |
| March 2020 | COVID-19 Pandemic | Liquidity crunch; foreign investors sold U.S. Treasuries to raise dollars, causing yields to spike[3] |
| August 2024 | BOJ Rate Hike to 0.25% | 12.4% Nikkei drop; $200 billion unwound in weeks; heavy sell-off in U.S. tech stocks[2][6] |
One major takeaway is that the rate of change in interest differentials often matters more than their absolute levels. Even minor adjustments can set off large-scale unwinding when leverage is high[2]. Additionally, these events rarely occur in isolation. For instance, after the 2008 crisis, it took until mid-2015 for the U.S. dollar to regain its pre-crisis standing against the yen[1].
The 2024 unwind also revealed a notable shift in behavior. Unlike March 2020 – when foreign investors sold U.S. Treasuries to raise cash, driving yields higher – the August 2024 event saw Treasury yields decline. This was because investors sold equities and used bonds as a hedge against currency risk[3].
"The carry trade works when volatility is low, but if that volatility goes up, people will unwind positions." – Yusuke Miyairi, FX Strategist, Nomura[8]
What’s Driving the Current Yen Carry Trade Unwind
Bank of Japan Policy Changes
The Bank of Japan (BoJ) has officially closed the chapter on its ultra-loose monetary policy. By late 2025, the BoJ raised its short-term policy rate to 0.75%, marking the highest level Japan has seen in three decades[10]. This significant change ends years of negative rates, which had been a cornerstone for yen-funded carry trades.
At the same time, the U.S. Federal Reserve has been moving in the opposite direction, cutting its target range to 3.5%–3.75%[10]. As a result, the rate differential between Japan and the U.S. has shrunk from over 5% in early 2024 to about 3% by late 2025[10]. For carry traders, this narrowing gap directly reduces the profit margin – or "positive carry" – from borrowing yen to invest in higher-yielding assets elsewhere.
Adding to this shift, the BoJ has rolled out a quantitative tightening (QT) plan, halving its monthly bond purchases from ¥6 trillion to ¥3 trillion by the first quarter of 2026[9]. This move tightens market liquidity and pushes yields higher, making it costlier to borrow yen.
"It’s the rate of change (of interest rate differentials) that matters. And so if the BOJ are stepping up the pace of rate hikes relative to market pricing… then the pressure on the carry trade increases." – James Malcolm, Head of FX Strategy at UBS[8]
These policy changes are also reshaping Japan’s government bond market, creating ripple effects across investor strategies.
Rising Japanese Government Bond Yields
Japan’s 10-year government bond (JGB) yields climbed to 2.015% in December 2025, a level not seen since August 1999[10]. This rise marks a clear break from decades of near-zero rates. With JGB yields now at 2.015%, Japanese investors are increasingly pulling capital back from lower-yielding foreign bonds, finding domestic bonds more appealing – even after factoring in the cost of currency hedging.
The impact of rising JGB yields goes beyond just investment decisions. The yen’s traditional role as a safe-haven currency has been affected. Climbing yields have, at times, weakened the yen during yield spikes, undermining its reputation as a stable refuge during market turbulence[11]. For carry traders who relied on the yen’s predictable behavior, this adds a new layer of complexity.
As bond yields reshape investor preferences, they also amplify market volatility, accelerating the unwinding of carry trades.
Market Volatility and Currency Price Movements
The yen carry trade thrives in calm, stable markets, making it highly sensitive to rising volatility[10]. When markets become turbulent, even modest rate changes can force traders to scale back positions to stay within risk limits.
The USD/JPY pair has seen dramatic fluctuations. For instance, after the BoJ’s July 2024 rate hike, the dollar fell from 161.9 yen to 150.2 yen – a drop of more than 10 yen in under a month[8]. On August 5, 2024, a sudden 3% yen surge triggered a global market sell-off, with the Nikkei 225 plunging over 12%[2][11]. These sharp moves create a feedback loop: rising volatility leads to margin calls, forcing traders to buy back yen and sell assets, which in turn fuels more volatility.
Analysts have identified the 155–156 range for USD/JPY as a potential "soft intervention threshold." Japan’s Ministry of Finance may issue verbal warnings or take direct action if the yen strengthens beyond this range[5][10]. Traders often monitor Bollinger Bands on USD/JPY charts to detect expanding volatility, which can signal an impending carry trade correction[5].
As volatility rises, margin calls and rapid position adjustments become unavoidable, further destabilizing the market. These shifting dynamics highlight the need for traders to rethink their strategies in light of the ongoing yen carry trade unwind.
Market Effects and Trading Strategies for Unwinds
Orderly vs. Disorderly Unwinds: Market Effects
Carry trade unwinds can unfold in very different ways. The key distinction between an orderly adjustment and a disorderly panic lies in how quickly traders need to exit their positions – and whether the market can handle the selling pressure without breaking down.
An orderly unwind typically happens alongside gradual policy changes, giving markets time to adjust. On the other hand, a disorderly unwind is often triggered by unexpected rate hikes or sudden spikes in volatility, forcing traders to exit positions in a hurry.
Take the August 2024 unwind as an example of disorderly market behavior. When the Bank of Japan (BoJ) unexpectedly raised rates, around $200 billion in carry trades were unwound within just two to three weeks [2]. The fallout was severe: the Nikkei 225 saw its worst single-day loss since 1987, while U.S. tech stocks – especially in the Nasdaq – took a significant hit as Japanese investors sold off their most profitable assets to cover yen-denominated loans [2].
Here’s a quick comparison of how orderly and disorderly unwinds affect major asset classes:
| Feature | Orderly Unwind | Disorderly Unwind |
|---|---|---|
| Market Trigger | Gradual BoJ policy adjustments | Sudden rate hikes or geopolitical shocks |
| Equity Impact | Manageable sector rotation and pullbacks | Sharp sell-offs; steep declines in tech and Nikkei stocks |
| Currency Move | Slow yen appreciation with verbal MoF warnings | Rapid yen rallies; direct market interventions |
| Bond Market | Gradual capital repatriation | High volatility; initial "flight to safety" followed by forced selling |
| Liquidity | Tight but operational | Severe liquidity crunch; wider bid-ask spreads; margin calls |
The effects of these unwinds ripple across various markets. High-yield currencies like the Mexican peso and Australian dollar often weaken as traders exit carry positions. Speculative assets, including cryptocurrencies and emerging market debt, face downward pressure as global liquidity tightens. Bonds typically go through a two-step reaction: yields drop initially during a "flight to safety", but this is often followed by selling pressure from Japanese investors repatriating capital [12].
Trading Approaches During Unwinds
Given the potential market impacts, traders must adapt their strategies to navigate these turbulent periods. One key area of focus is the 155–156 USD/JPY range. Breaching this range often signals accelerating unwind pressure [5][10].
Another critical indicator is the yield spread between U.S. Treasuries and Japanese Government Bonds (JGBs). When JGB yields rise above 1.7% and stay there, Japanese institutional investors – who collectively hold about $2.5 trillion in U.S. securities – may begin selling foreign assets to reinvest domestically. This can push the yen higher while putting downward pressure on U.S. markets [13].
Volatility indicators also play a crucial role. For instance, Bollinger Bands on USD/JPY charts can reveal expanding volatility, often a precursor to sharp corrections. If the bands widen significantly and the Relative Strength Index (RSI) shows overbought conditions, it could indicate that bullish momentum for the yen is nearing its limit. Key USD/JPY support levels to watch include 153.00, 150.00, and 146.45 [5].
Additionally, since Japanese investors frequently sell U.S. tech stocks to cover yen shorts, traders with Nasdaq exposure should consider hedging their positions during periods of sudden yen strength. Watching cross-currency pairs like MXN/JPY or AUD/JPY can also provide early clues about broader equity market sell-offs [3].
Using TraderVPS for Better Trade Execution
TraderVPS Features for Carry Trade Strategies
When yen carry trades unwind, the stakes are incredibly high. Take the August 2024 event, for instance – an estimated $200 billion in positions were liquidated within just two to three weeks [2]. During these moments, liquidity can disappear, price gaps widen, and execution speed becomes absolutely critical. That’s where TraderVPS steps in. Its low-latency infrastructure is designed to process orders in milliseconds, minimizing slippage and ensuring you stay ahead in fast-moving markets. This kind of performance directly addresses the execution challenges that arise during volatile carry trade unwinds [14].
TraderVPS also guarantees 24/7 uptime, which is essential for navigating Bank of Japan policy announcements that often occur outside regular U.S. trading hours. Built specifically for platforms like NinjaTrader, TraderVPS combines NVMe storage, AMD EPYC processors, and multi-monitor support to handle high-volume data streams seamlessly. This allows you to monitor complex cross-market flows – like movements in USD/JPY, U.S. Treasuries, and global equities – in real time, even during periods of extreme stress [6].
Selecting the Right TraderVPS Plan
Choosing the right VPS plan is key to managing the demands of high-volatility trading. TraderVPS offers several options tailored to different trading needs:
- VPS Lite ($69/month): Includes 4 AMD EPYC cores, 8GB of RAM, support for 1–2 charts, basic automated strategies, and single-monitor functionality. Ideal for traders with simpler setups.
- VPS Pro ($99/month): Designed for active traders, this plan features 6 cores, 16GB of RAM, support for 3–5 charts, and dual-monitor capabilities.
- VPS Ultra ($199/month): Built for high-frequency trading, offering 24 cores, 64GB of RAM, and support for up to 4 monitors. Perfect for navigating chaotic markets.
- Dedicated Server ($299/month): The top-tier option for institutional-grade execution. It includes 12+ AMD Ryzen cores, 128GB of RAM, 2TB+ NVMe storage, 10Gbps+ network speeds, and support for up to 6 monitors – capable of handling 7+ charts with ease.
Higher resource allocations in these plans ensure your system can handle the message traffic spikes that often accompany volatile market conditions. This flexibility allows you to optimize your trading strategy without worrying about technical limitations.
Improving Trading Performance With TraderVPS
In volatile markets, having the right infrastructure can make all the difference. TraderVPS provides the tools needed to execute protective orders and manage risks effectively. For instance, its high-speed NVMe storage allows you to backtest strategies against historical unwind events, helping you fine-tune risk limits and margin rules in anticipation of future market swings [14].
During active carry trade unwinds, dedicated resources ensure your platform doesn’t freeze under the pressure of peak trading volumes. Whether you’re monitoring critical USD/JPY levels or tracking JGB yields as they approach 2%, TraderVPS keeps your NinjaTrader platform stable. This reliability is crucial for executing stop-losses and managing cascading margin calls, even when liquidity dries up. With TraderVPS, you can trade confidently, knowing your infrastructure won’t let you down when it matters most.
Conclusion: Managing the Yen Carry Trade Unwind
The unwinding of yen carry trades is a complex, multi-year process that can significantly influence global markets. Historical trends suggest these unwinds take time, with some analysts estimating that only about half of the carry trade had been reversed following the initial market turmoil in August 2024 [2].
Recent shifts in the Bank of Japan’s (BoJ) policies have dramatically changed the carry trade dynamics. The era of ultra-low rates is over, as rising Japanese Government Bond (JGB) yields encourage Japanese institutional investors to bring capital back home instead of seeking higher returns abroad [14]. This shift has added persistent pressure on the USD/JPY exchange rate and led to widespread selling in heavily crowded trades, particularly impacting U.S. momentum stocks and tech sectors [4].
Unlike past financial crises, today’s unwinds are more about funding repricing than systemic insolvency [4]. While these events can lead to sharp asset price swings and liquidity challenges, they don’t necessarily indicate broader credit crises. The real risk lies in execution challenges – widening bid–ask spreads, sudden price gaps, and cascading margin calls. In such volatile moments, having reliable infrastructure is critical. Traders need platforms with low-latency execution to exit positions swiftly, systems that operate 24/7 to respond to unexpected BoJ announcements, and stable technology that won’t fail during periods of extreme market stress [14][15].
"Until the yen stabilizes, it is hard to see how global equity market volatility declines."
– Nicholas Colas, Co-founder, DataTrek [6]
For carry trades to resume, markets need lower volatility and clearer guidance on future BoJ policies [1]. Until that clarity emerges, traders should keep a close eye on interest rate differentials, as the speed of change can often have a greater impact than the absolute levels [2]. Monitoring key technical levels, such as ¥130 to the USD, may provide psychological support markers. Additionally, hedging currency exposure can be a more strategic approach than liquidating entire positions [1]. Above all, position sizing should account for current volatility, as leverage can significantly amplify losses during sudden price movements [14].
Navigating these unwinds successfully depends on strong risk management and reliable trading infrastructure. Platforms with low-latency execution are essential to managing these shifts effectively. When liquidity evaporates and every millisecond counts, tools like TraderVPS offer the speed, uptime, and stability needed to help traders manage risk and avoid catastrophic slippage.
FAQs
What impact does the yen carry trade have on global market volatility?
The yen carry trade works by taking advantage of Japan’s low interest rates. Investors borrow yen at these lower rates and then invest the funds in assets that offer higher returns elsewhere. However, when unexpected events occur – like an interest rate hike by the Bank of Japan or sudden market intervention – the yen can strengthen rapidly. This often forces investors to unwind their trades, causing a ripple effect across financial markets.
When these trades are reversed, the impact can be enormous. With the yen carry trade estimated to involve hundreds of billions of dollars, the unwinding process can trigger sharp market corrections. Stock indices may tumble, and volatility measures, such as the VIX, can spike. Essentially, the yen carry trade plays a major role in shaping global market dynamics, and its unwinding can lead to significant price swings and heightened uncertainty.
How do rising Japanese government bond yields affect global investors?
Rising yields on Japanese government bonds (JGBs) can ripple through global markets by pushing up borrowing costs. This trend often triggers a yen carry trade unwind, where Japanese investors pull their funds back to domestic markets. Such moves can spark large-scale capital outflows, fueling heightened volatility in both global equity and bond markets.
For international investors, this scenario brings potential challenges like fluctuating currency values, steeper financing costs, and greater exposure to risk. Staying updated on these developments and implementing solid risk management strategies is crucial to navigating these unpredictable market conditions.
Why are changes in interest rate differentials important for carry trades?
Carry trades work by taking advantage of the gap between the interest rates of the currency you borrow and the one you invest in. But when this interest rate gap shrinks – or flips entirely – the potential returns drop, making the trade far less appealing. In such cases, traders often abandon these positions in search of better opportunities.
Unexpected changes in interest rate policies or market dynamics can make these shifts even more dramatic, leading to quick and sometimes volatile currency market reactions. For traders, keeping a close eye on these changes is critical for managing risks and spotting the right moments to enter or exit trades.








